Animal Welfare – An Overview of Key Topics and Issues
Billions of mammals, tens of billions of birds, and trillions of insects and aquatic animals live terrible lives in intensive housing systems such as factory farms Animal welfare is a crucial area of concern for those looking to do the most good.
In this overview, we’ll explore the ethical arguments for prioritising animal welfare and how individuals can take high-impact actions to protect animals.
What Is Animal Welfare?
Animal welfare refers to the physical and psychological well-being of animals. It is a broad term that includes negatives, such as the stress and injury caused by breeding, housing, transport and slaughter, as well as positives, such as the ability to display natural and normal social behaviour.Efforts to improve animal welfare focus reducing pain and stress involved in raising animals, or on reducing the number of animals raised in industrial settings altogether.
Animal Welfare Across Different Contexts
1. Farmed Animals
The majority of suffering happens in industrial-scale farming. Chickens, pigs, cows, fish and other animals reared for their meat, eggs, milk, skin, and fur often live in overcrowded conditions with minimal veterinary care. Countries around the world have different laws and regulations surrounding the raising, care, and transportation of livestock animals, with some countries having stricter, more welfare-focused laws than others.


2. Wild Animal Welfare
While less visible, wild animals also face immense suffering from habitat loss, starvation, disease, and predation from both other animals and poachers. Though it’s a more complex area, wildlife advocates argue for scalable interventions such as vaccination programmes, habitat improvement, and research funding to find out how humans can help animals in the wild in a way that is ecologically sound.
3. Companion Animals
Companion animal welfare refers to the health, well-being, and humane treatment of animals that people keep primarily for company, such as dogs, cats, rabbits, birds, and other small animals. Companion animal welfare is different in many countries, with some having softer or non-existent regulations that lead many to be abandoned, abused, or killed each year.
What Context of Animal Welfare is the Effective Altruism Community Concerned With?
Factory farming is a central concern for the Effective Altruism community due to the immense scale of suffering it causes and the potential for cost-effective interventions to alleviate that suffering. Each year, tens of billions of terrestrial animals—particularly chickens, pigs, and cows—are raised in industrial agricultural systems where they often endure severe confinement, lack of environmental enrichment, painful procedures without anesthesia, and early slaughter. The number of aquatic animals and insects caught and bred is ever larger, and these animals are arguably even more neglected, even by animal advocates. When deciding among cause areas to devote time and resources to, the EA community generally relies on the Importance, Tractability, and Neglectedness (ITN) framework, which helps with determining how much impact could be achieved. This is further combined with EA’s core principle of doing the most good with limited resources.Why is Animal Welfare A Priority Cause Area in Effective Altruism?
1. The Scale of Animal Suffering
Over 100 billion animals are raised and killed for food each year, the vast majority in intensive factory farms where they endure extreme confinement, mutilation, and stressful conditions. Over a trillion aquatic animals are caught each year, with very limited attention to their welfare during catch and slaughter. In addition to farmed and caught animals, billions of animals suffer in animal testing, entertainment, and illegal wildlife trade.
Our World in Data reported in 2024 that over 500 billion animals are reared for consumption alone each year (see the breakdown below).
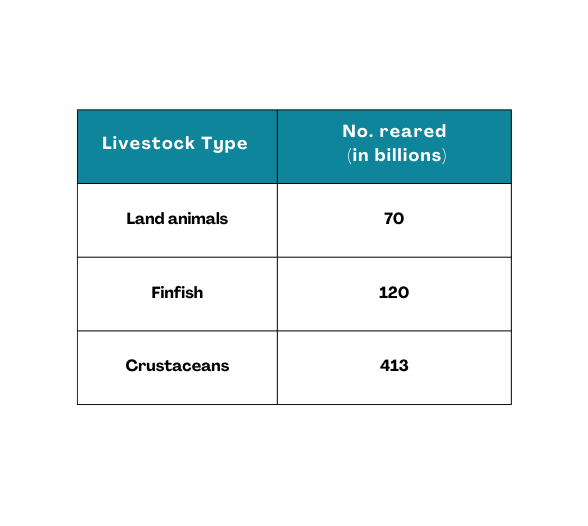

Improving farm animal welfare even slightly can lead to massive reductions in suffering due to the sheer number of animals affected.
2. Neglected cause area
Animal welfare is severely neglected relative to its importance. This is despite a seemingly high public support for the cause. In a survey by the European Commission in 2023, around 84% of Europeans believe that the welfare of farmed animals should be better protected in their country than it is now.
According to Open Philanthropy and Animal Charity Evaluators, it is one of the most cost-effective areas for philanthropic giving, with high room for funding and measurable impact through strategies such as corporate and public campaigning, or research and development of alternatives to animal products. Unfortunately, there is very little funding available to animal charities, and much less towards charities that specifically focus on the plight of factory farmed animals.
3. Non-human animals are sentient, therefore deserving of moral consideration
Briefly, sentience is defined as the ability to experience feelings and sensations that are intrinsically positive or negative to the individual. Scientific consensus confirms that many animals, including pigs, chickens, cows, fish, and insects, are capable of feeling pain, fear, and pleasure. Animal welfare advocates and animal rights philosophers argue that sentience is sufficient grounds to confer a moral status, and thus consideration in the form of laws, rights, and protections, to animals.
What Is Currently Being Done In Support of Animal Welfare?
There are many ways individuals and organisations can contribute to animal welfare. Here are the most effective actions based on EA research:
1. Funding effective animal charities
One of the highest-leverage ways to help animals is by donating to top-rated charities working on farm animal advocacy, corporate campaigns, and legislative reform.
Open Philanthropy, a philanthropic funding organisation, regularly provides grants to organisations they deem as having high impact in the area of animal welfare. These organisations work to secure corporate commitments, promote plant-based diets, and lobby for more pro-animal legislation and legal enforcement. There are many other local and international organisations that support animal welfare, either by funding research and interventions or evaluating the effectiveness of organisations, notably:
- Doneer Effectief (The Netherlands)
- Effective Altruism Animal Welfare Fund (international)
- Giving What We Can (international)
- Animal Charity Evaluators (international)
2. Reduction or elimination of animal product consumption
Reducing meat and dairy consumption directly reduces the demand for factory-farmed animals. There are various individual and collective ways to reduce or eliminate animal product consumption. On the supply-side, improving the available alternatives for consumers in terms of price, taste, health, convenience and availability is a promising way to reduce the demand for factory-farmed animals
3. Enacting policy change and regulation
Legislation is one of the most sustainable paths to long-term improvements in animal welfare. The European Convention for the Protection of Animals kept for Farming Purposes, a framework containing principles for the appropriate keep, care, and housing of animals, is based on 5 key ‘freedoms’. The Five Freedoms originated from a report, popularly referred to as the ‘Brambell Report’, following public outcry farming practices in England.
In the Netherlands, there are a number of resources publicly available to learn more about animal welfare and what kinds of policies and regulations are in place:
- National regulations on animal welfare for businesses
- Information from the Council of Animal Affairs
- Government website on animal welfare
- Dierenbescherming's ‘Beter Leven’ food label for retailers
Did you enjoy this page? You might also like these articles:
- Curious about how to build a career in animal advocacy?
Check out our Career in Animal Welfare guide. - How is AI being used in Animal Welfare?
Check out our article on AI x Animal Welfare - Interested in making a difference through donations?
Read our Donations in Animal Welfare guide. - Should we help animals in the wild? Learn more in our Wild Animal Welfare guide